Jenny Hill Jennifer.Hill@uwe.ac.uk
Associate Professor in Teaching and Learning
Chronosequences of ant nest mounds from glacier forelands of Jostedalsbreen, southern Norway: Insights into the distribution, succession and geo-ecology of red wood ants (Formica lugubris and F. aquilonia)
Hill, Jennifer; Vater, Amber; Geary, Andrew; Matthews, John
Authors
Amber Vater
Andrew Geary
John Matthews
Abstract
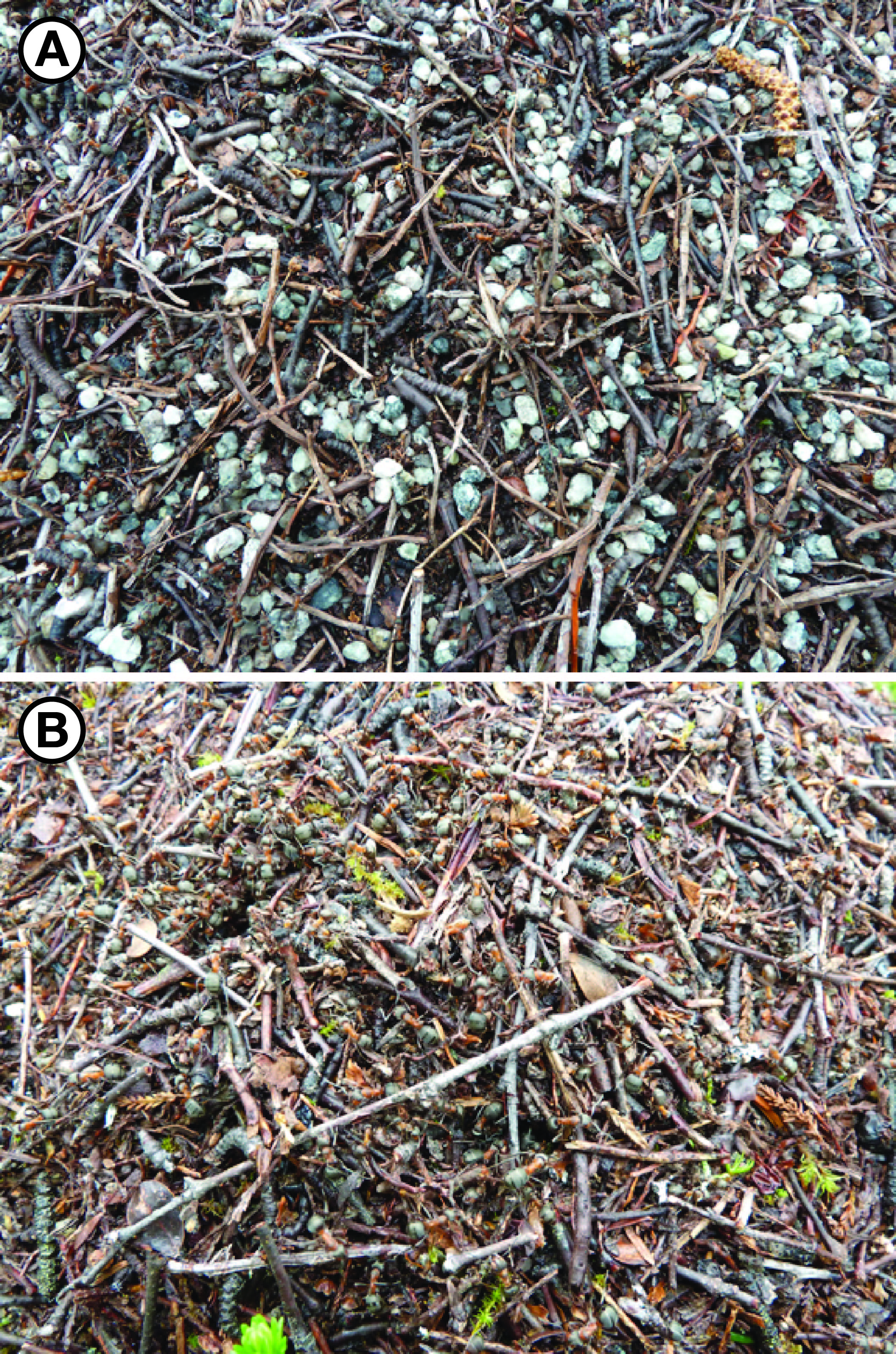
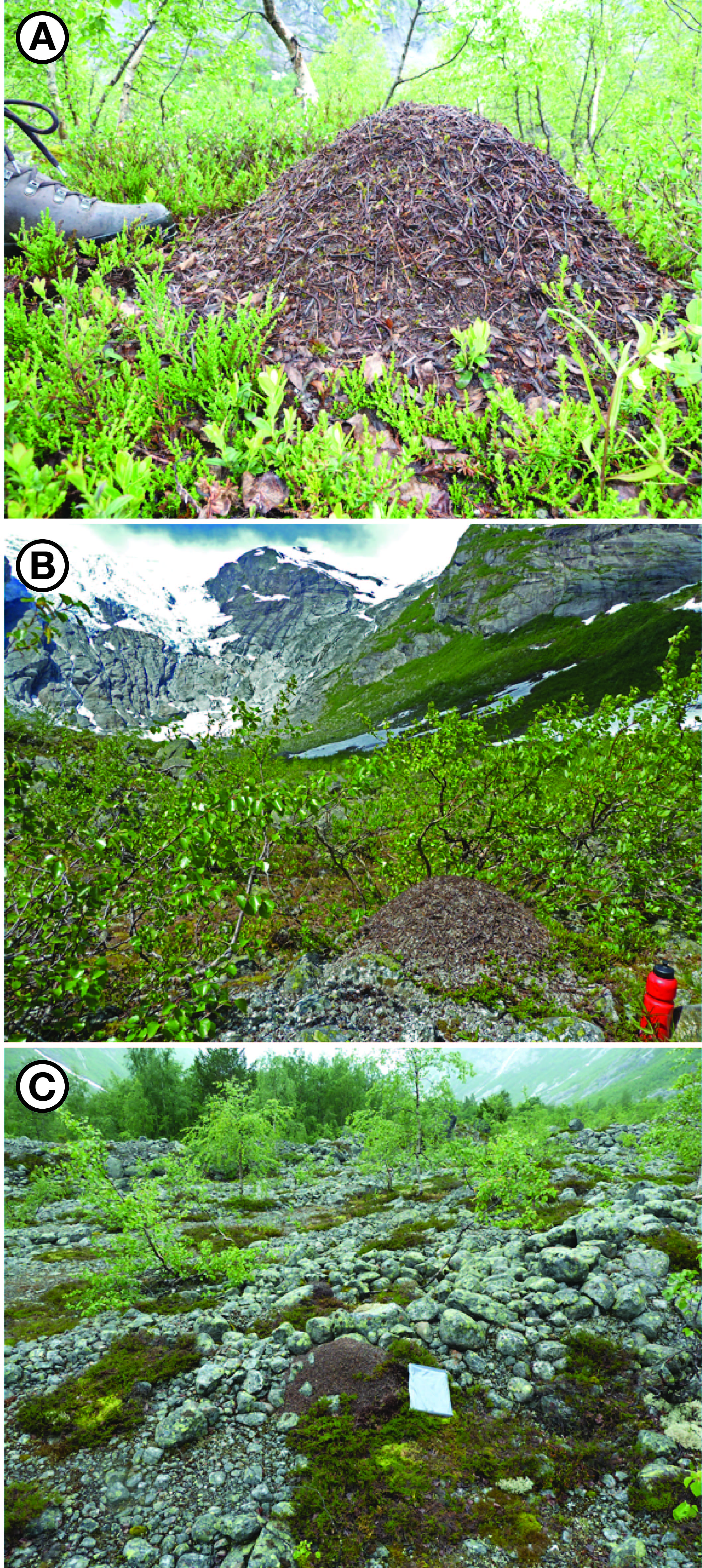
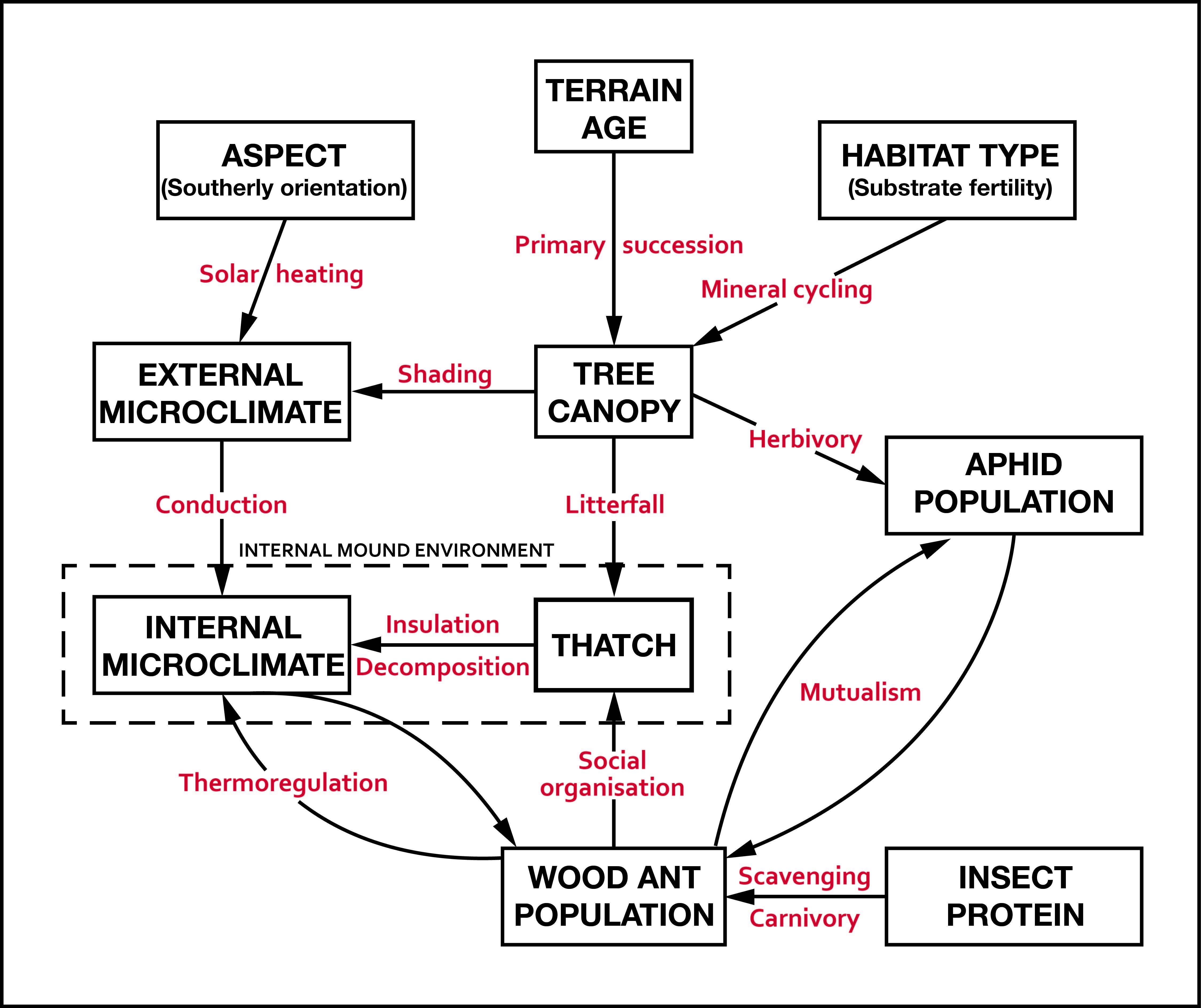
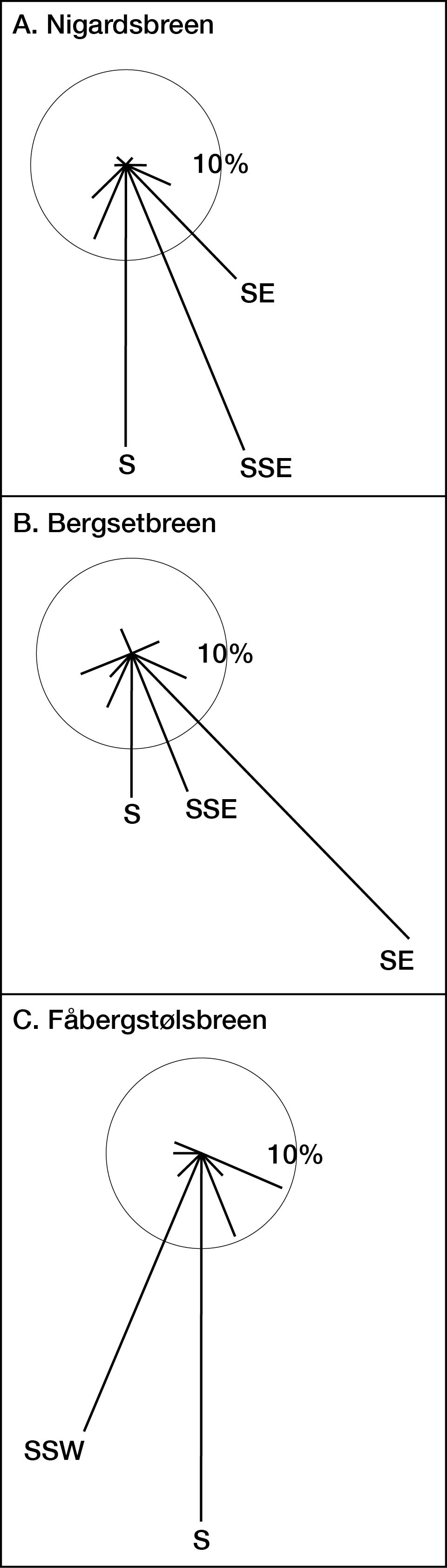
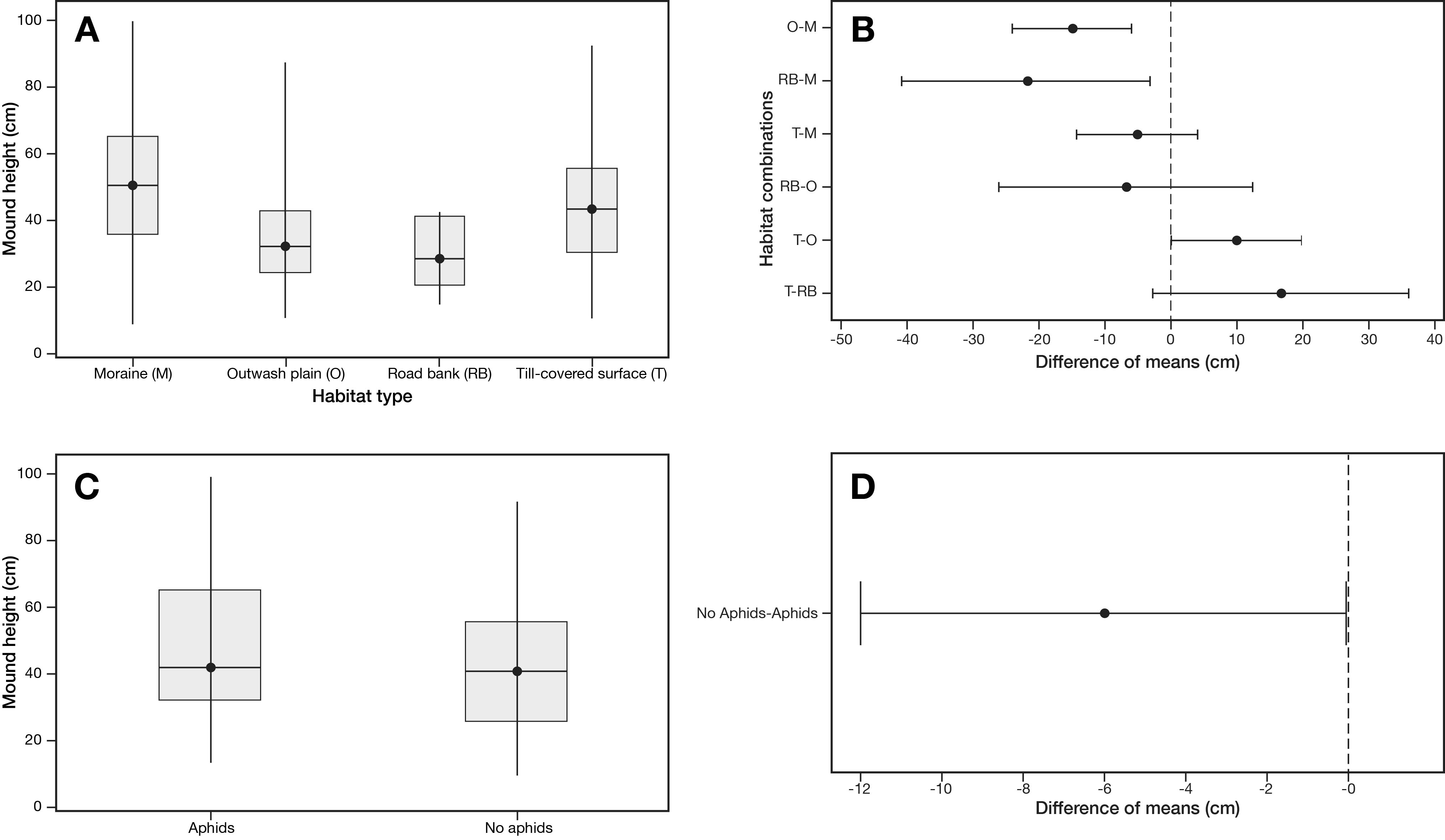
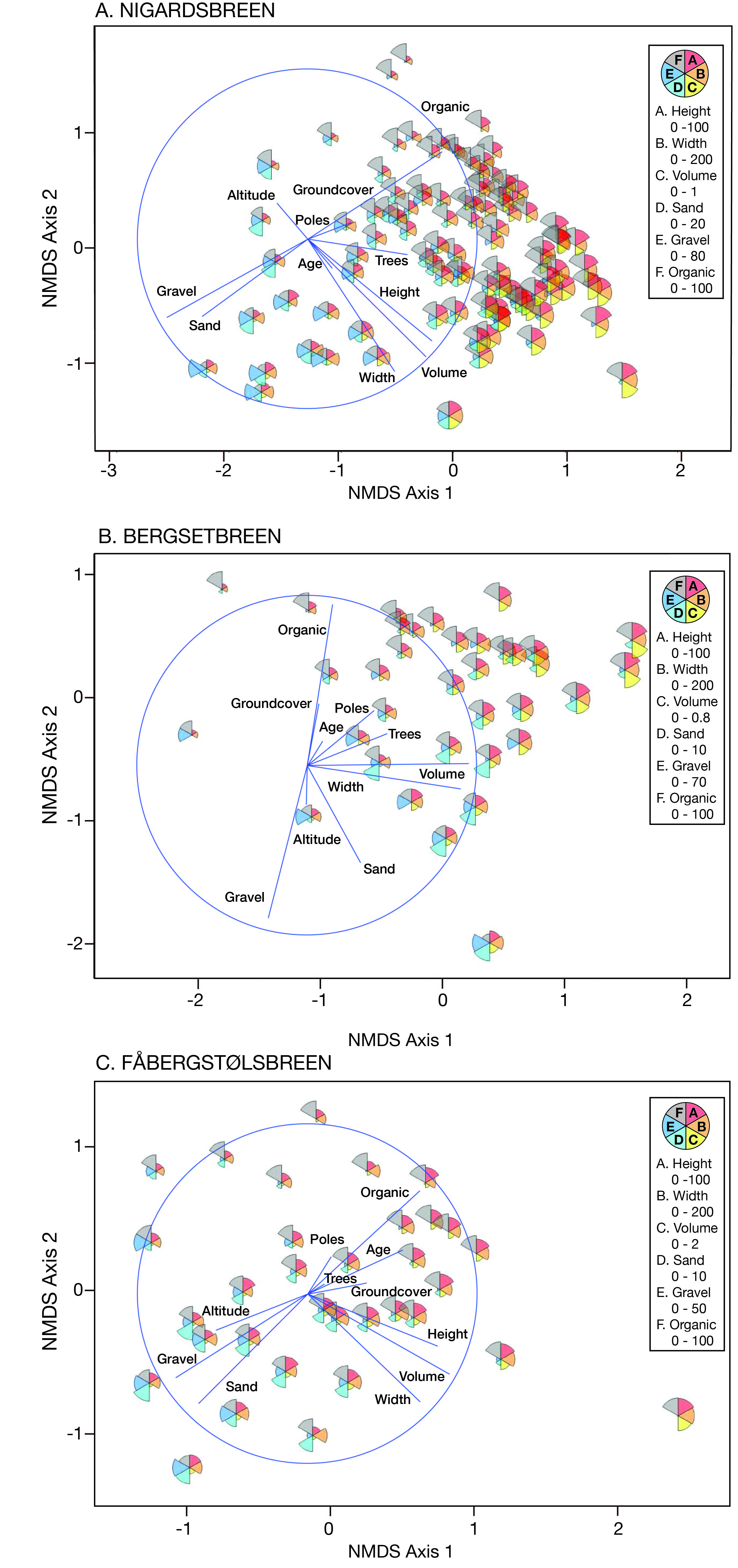
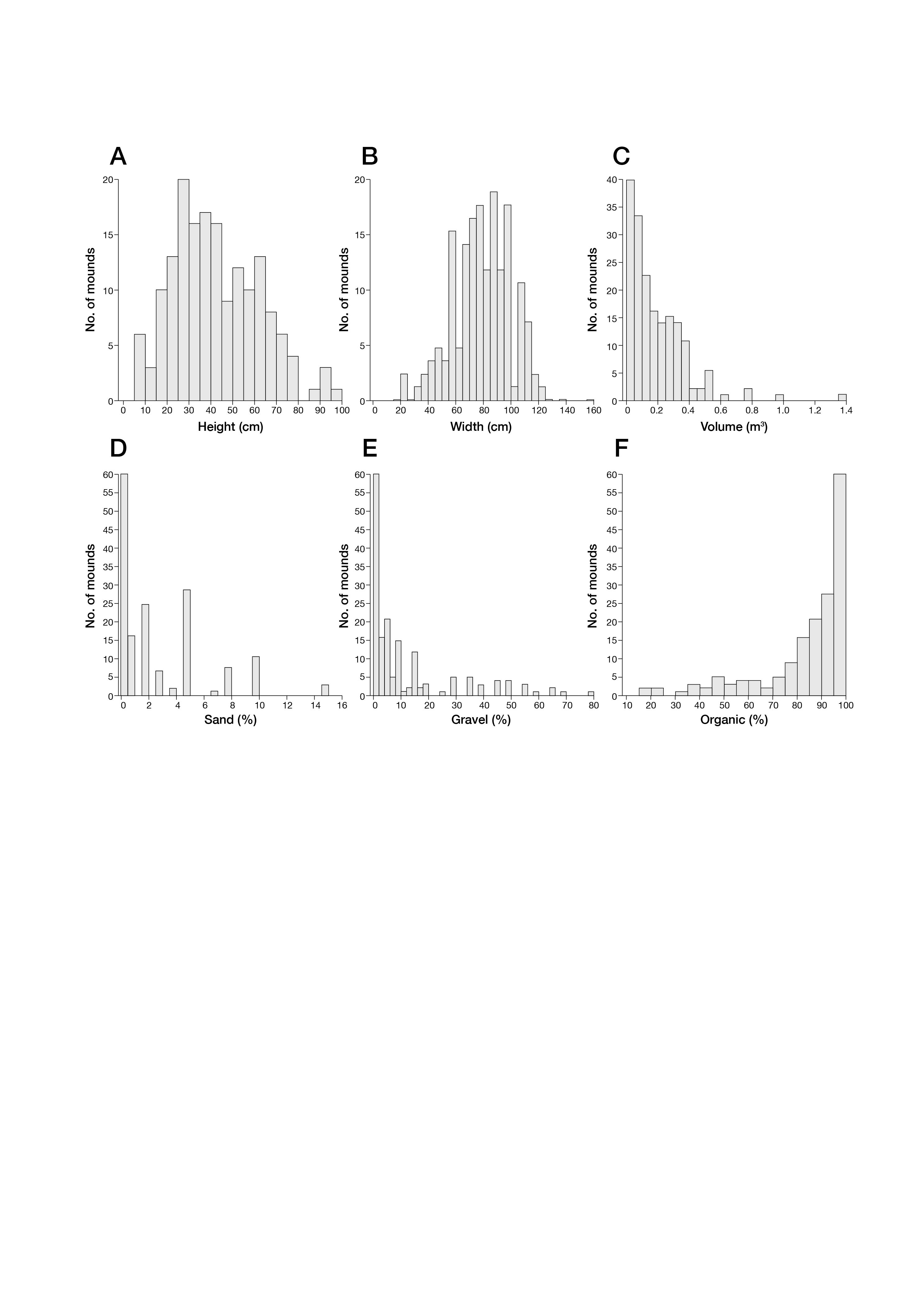
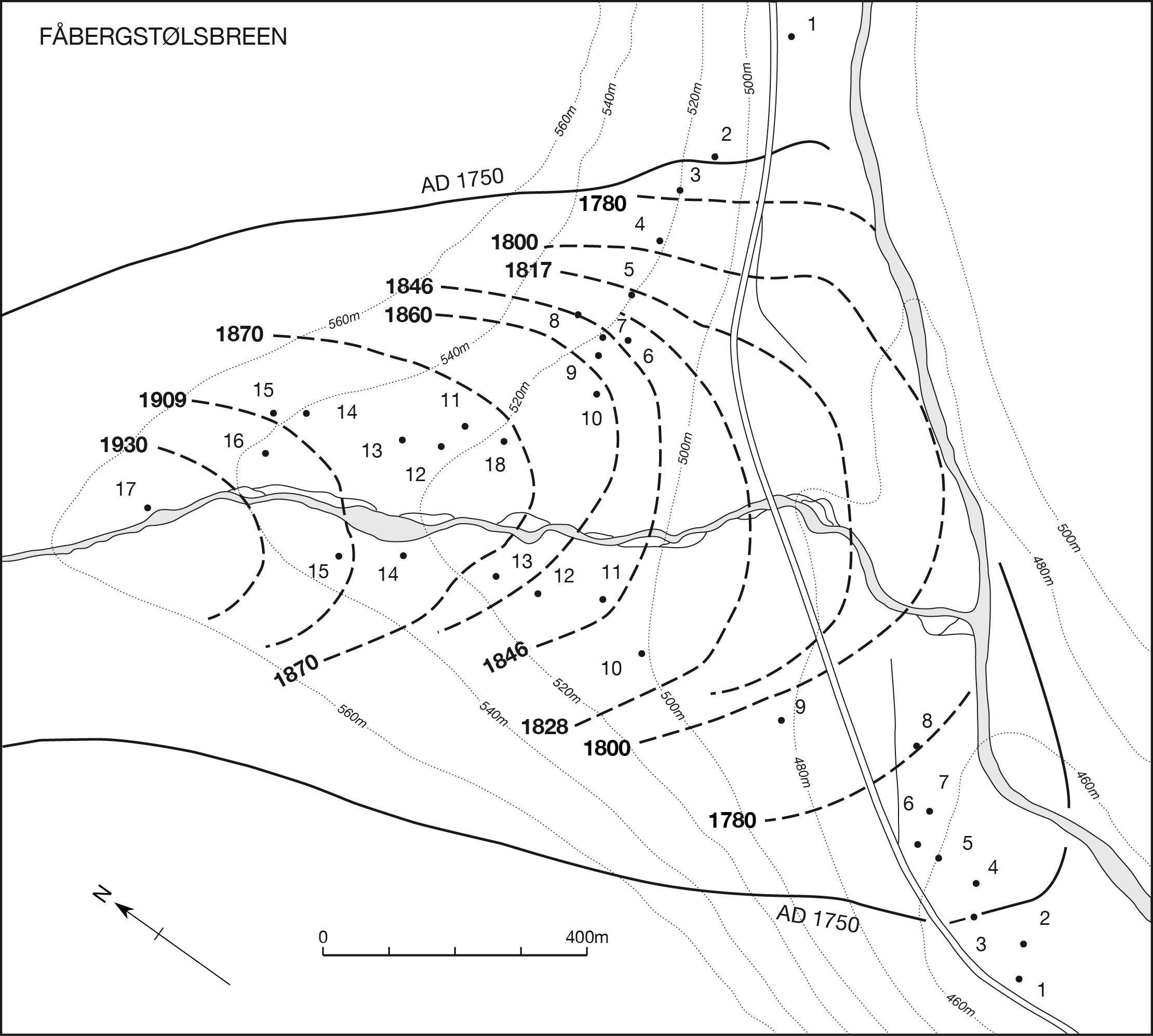
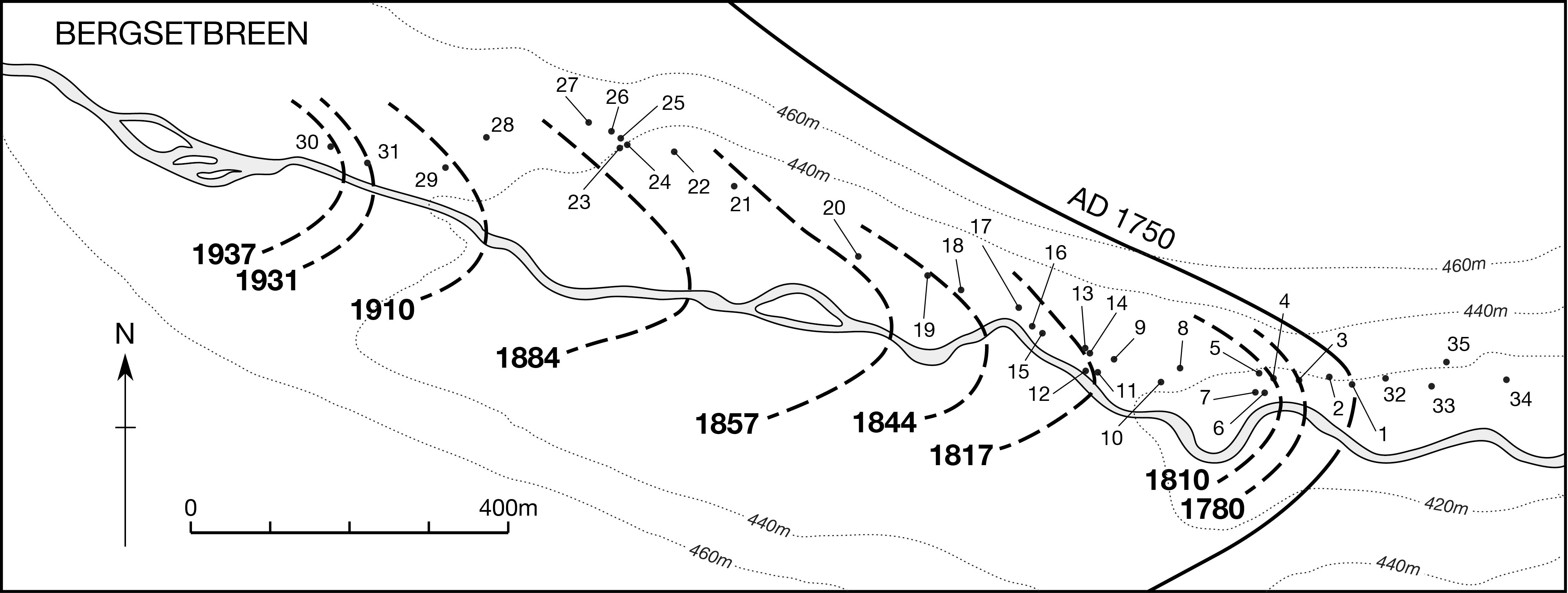
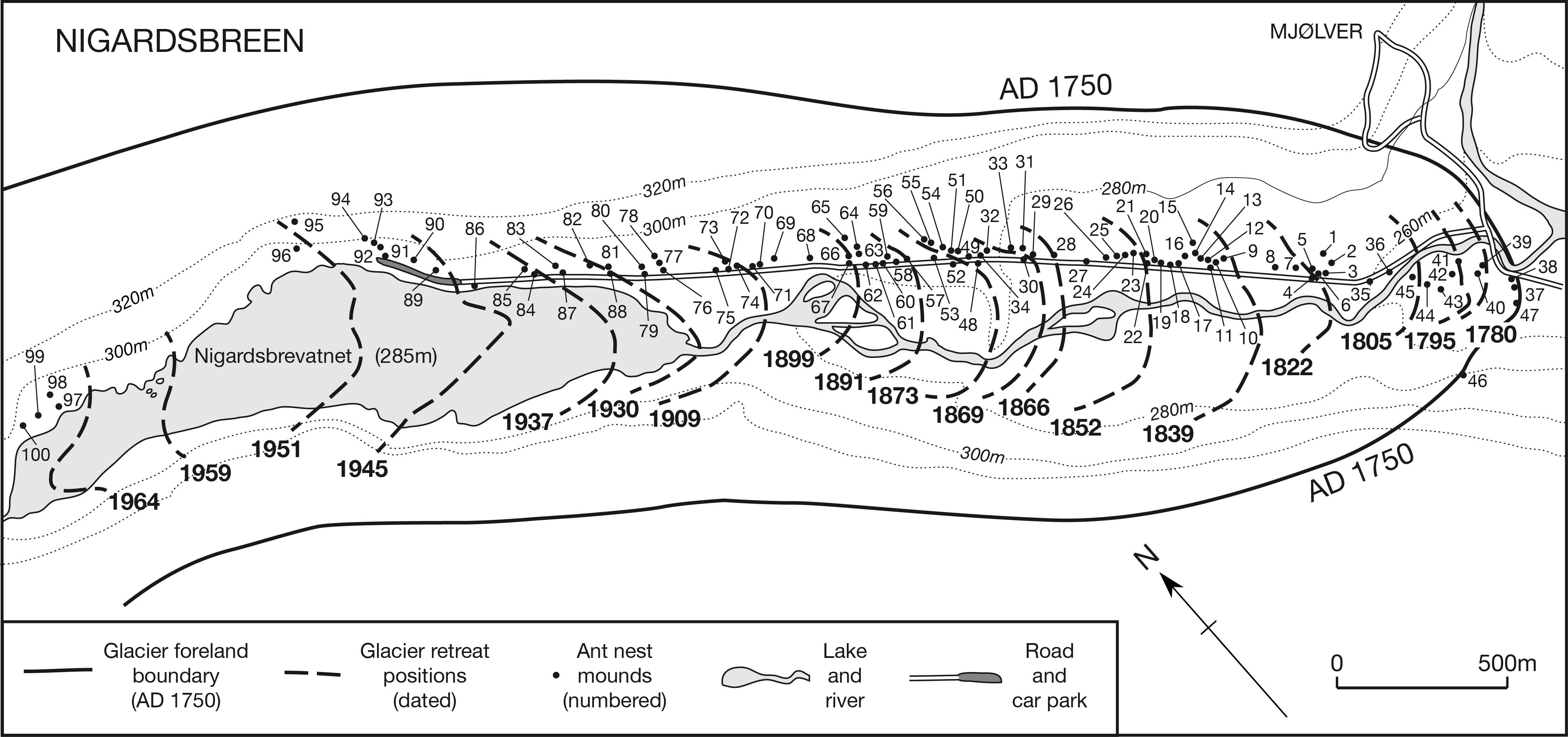
© 2018, The Author(s) 2018. Red wood ant nest mounds were investigated on terrain deglaciated since the mid-18th century at three outlet glaciers of the Jostedalsbreen ice cap in southern Norway. Chronosequence methodology was combined with a geo-ecological approach in the context of autecology. Size and composition of 168 mounds, most of which belonged to Formica lugubris, were related to terrain age, vegetation characteristics and physical habitat types using non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) linked to segmented bubble plots and inferential statistical techniques. Substantive insights include (1) colonisation occurs 50–80 years after deglaciation; (2) mounds up to 100 cm high occupy the glacier forelands with a density of 2.5–4.6 mounds/hectare; (3) the positive correlation between mound size and terrain age is weakened by the presence of numerous small mounds attributed to the expansion of polydomous colonies by budding; (4) although mounds are mostly composed of plant remains (litter), they contain up to 17% mineral material (mostly gravel) on relatively young terrain; (5) mound size and composition are related to the number of trees (Betula pubescens) occurring within 5 m of each mound, which reflects the availability of biological resources for mound thatch and ant food, the latter being primarily honeydew from aphids; (6) where aphids are present on trees, the mounds tend to be relatively large, reflecting the presence of ant–aphid mutualism; (7) mounds are larger on moraines and till plains than on outwash deposits, probably reflecting the enhancement of tree growth because of greater moisture availability and soil fertility in the former habitat types; (8) a strong southerly preferred aspect in mound orientation indicates the importance of direct solar radiation in maintaining internal mound temperatures and (9) glacier-foreland landscapes are not simply time-dependent chronosequences reflecting succession but the product of spatio-temporal dynamics involving biotic and abiotic interactions, which we summarise in a conceptual geo-ecological model. The main methodological implications are that chronosequences can be used to investigate the autecology of keystone species using a geo-ecological approach and multivariate analysis.
Citation
Hill, J., Vater, A., Geary, A., & Matthews, J. (2018). Chronosequences of ant nest mounds from glacier forelands of Jostedalsbreen, southern Norway: Insights into the distribution, succession and geo-ecology of red wood ants (Formica lugubris and F. aquilonia). Holocene, 28(7), 1113-1130. https://doi.org/10.1177/0959683618761551
| Journal Article Type | Article |
|---|---|
| Acceptance Date | Jan 3, 2018 |
| Online Publication Date | Apr 29, 2018 |
| Publication Date | Jul 1, 2018 |
| Deposit Date | Jan 9, 2018 |
| Publicly Available Date | Feb 5, 2018 |
| Journal | Holocene |
| Print ISSN | 0959-6836 |
| Electronic ISSN | 1477-0911 |
| Publisher | SAGE Publications |
| Peer Reviewed | Peer Reviewed |
| Volume | 28 |
| Issue | 7 |
| Pages | 1113-1130 |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1177/0959683618761551 |
| Keywords | red wood ants, Formica spp., ant nest mounds, glacier foreland chronosequences, geo-ecological approach, southern Norway |
| Public URL | https://uwe-repository.worktribe.com/output/863498 |
| Publisher URL | https://doi.org/10.1177/0959683618761551 |
Files
ANTS - Fig.14 - revised.jpg
(1.6 Mb)
Image
ANTS - Fig.13 A-B mound composition.jpg
(4 Mb)
Image
ANTS - Fig.12 A-D Aspect.jpg
(152 Kb)
Image
ANTS - Fig.11 A-D - Box plots and Tukey plots.jpg
(315 Kb)
Image
ANTS - Fig.10 A-C NMDS ordinations.jpg
(2.1 Mb)
Image
ANTS - Fig.9 A-D - Regression lines.tif
(412 Kb)
Other
ANTS - Fig.8A-D - mound size.jpg
(6.8 Mb)
Image
ANTS - Fig.7 - histograms - revised.jpg
(342 Kb)
Image
ANTS - Fig.6 - Aphids.JPG
(3.1 Mb)
Image
ANTS - Fig.5 A-C - Introduction.jpg
(5 Mb)
Image
ANTS - Fig.4 - Fabergstolsbreen.jpg
(325 Kb)
Image
ANTS - Fig.3 - Bergsetbreen.jpg
(423 Kb)
Image
ANTS - Fig.2 - Nigardsbreen.jpg
(714 Kb)
Image
ANTS - Fig. 1 - Location map.tif
(313 Kb)
Other
ANTS - FINAL TEXT.pdf
(534 Kb)
PDF
You might also like
Storage of MPs in Channel sediments
(2023)
Presentation / Conference
The benefits and challenges of online learning during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons for future blended learning
(2023)
Presentation / Conference
Reflecting on the benefits and challenges of online learning during the COVID-19 Pandemic
(2022)
Presentation / Conference
Downloadable Citations
About UWE Bristol Research Repository
Administrator e-mail: repository@uwe.ac.uk
This application uses the following open-source libraries:
SheetJS Community Edition
Apache License Version 2.0 (http://www.apache.org/licenses/)
PDF.js
Apache License Version 2.0 (http://www.apache.org/licenses/)
Font Awesome
SIL OFL 1.1 (http://scripts.sil.org/OFL)
MIT License (http://opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.html)
CC BY 3.0 ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)
Powered by Worktribe © 2024
Advanced Search