John A. Matthews
Age and development of active cryoplanation terraces in the alpine permafrost zone at Svartkampan, Jotunheimen, southern Norway
Matthews, John A.; Wilson, Peter; Winkler, Stefan; Mourne, Richard W.; Hill, Jennifer L.; Owen, Geraint; Hiemstra, John F.; Hallang, Helen; Geary, Andrew P.
Authors
Peter Wilson
Stefan Winkler
Richard Mourne Richard.Mourne@uwe.ac.uk
Senior Lecturer
Jenny Hill Jennifer.Hill@uwe.ac.uk
Associate Professor in Teaching and Learning
Geraint Owen
John F. Hiemstra
Helen Hallang
Andrew P. Geary
Abstract
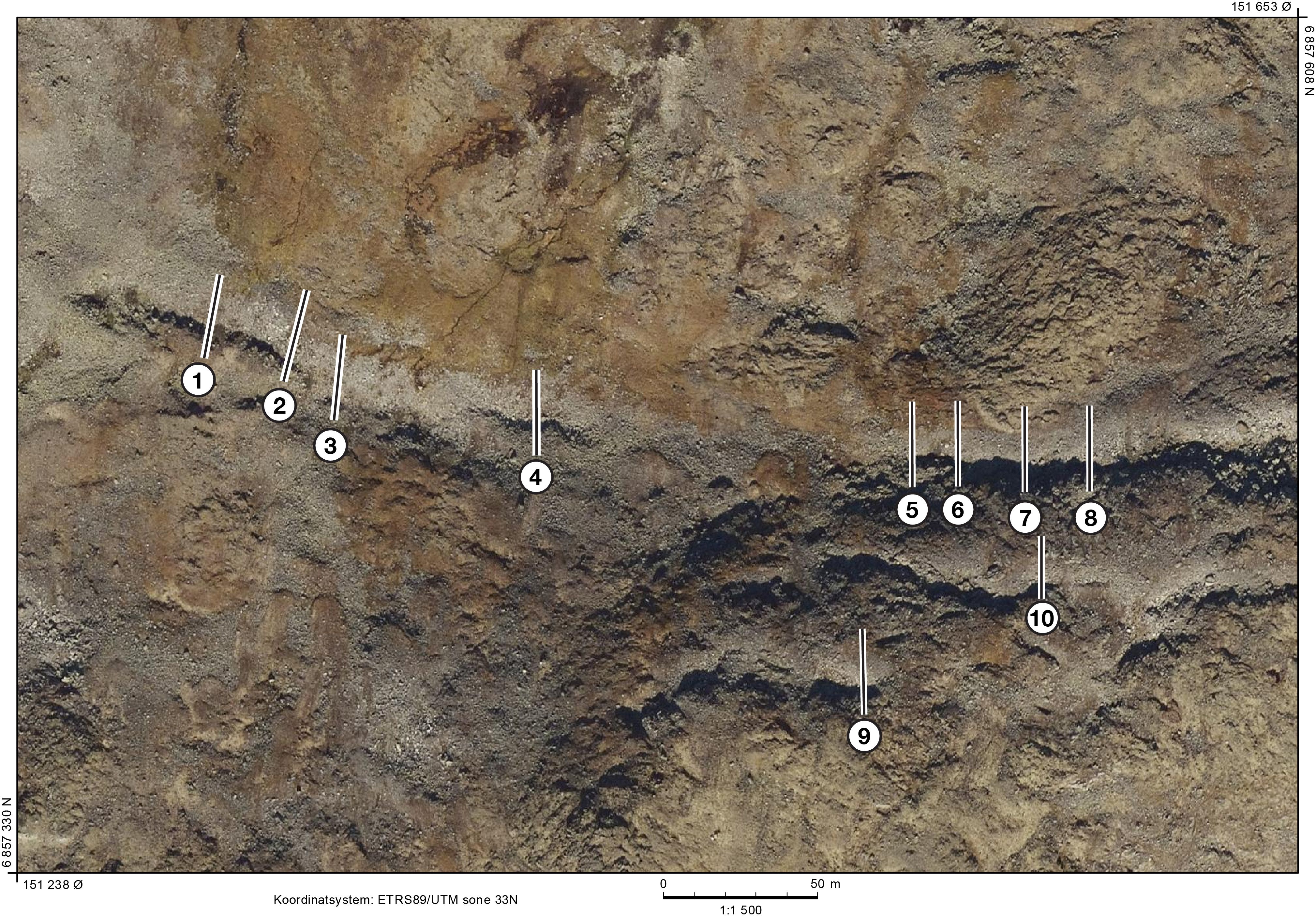
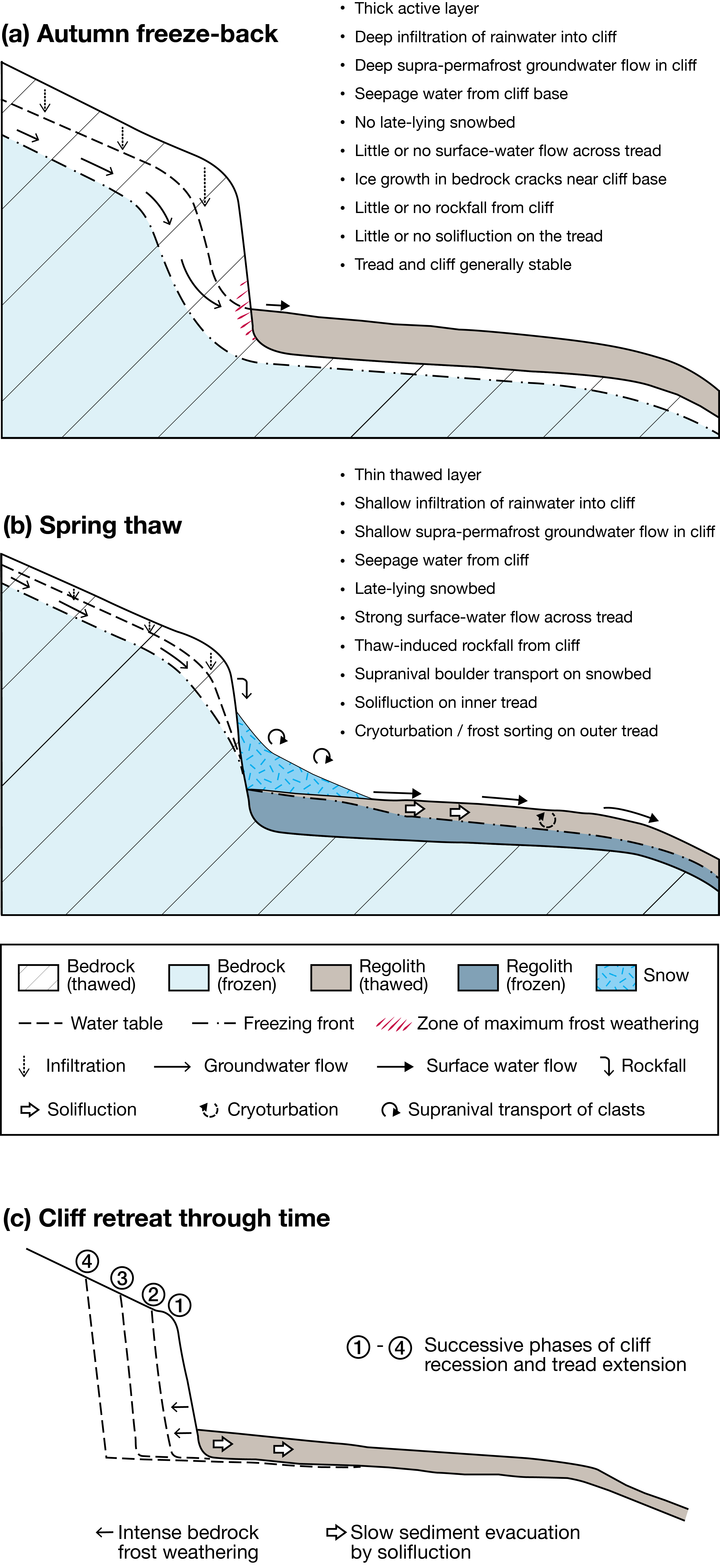
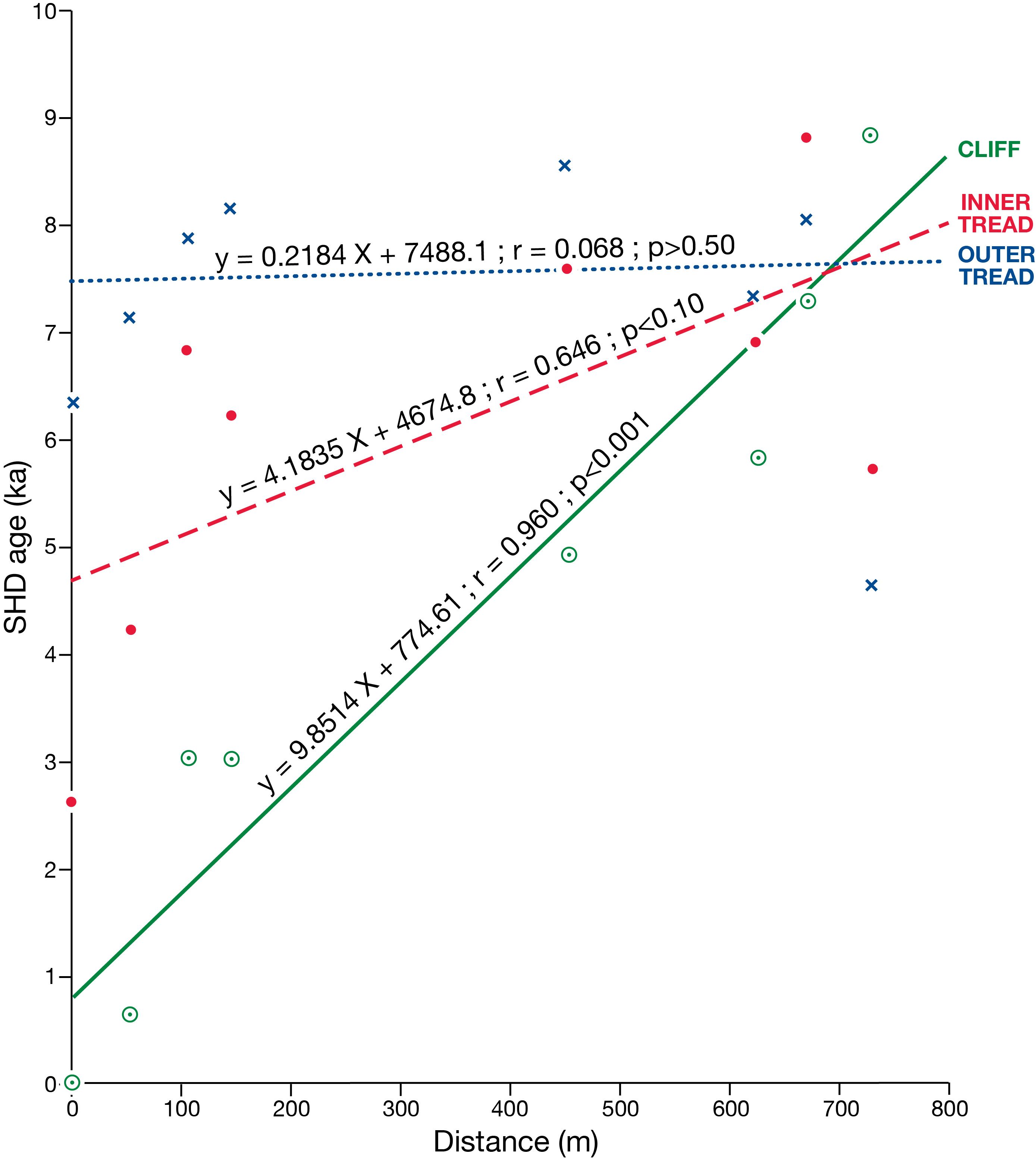
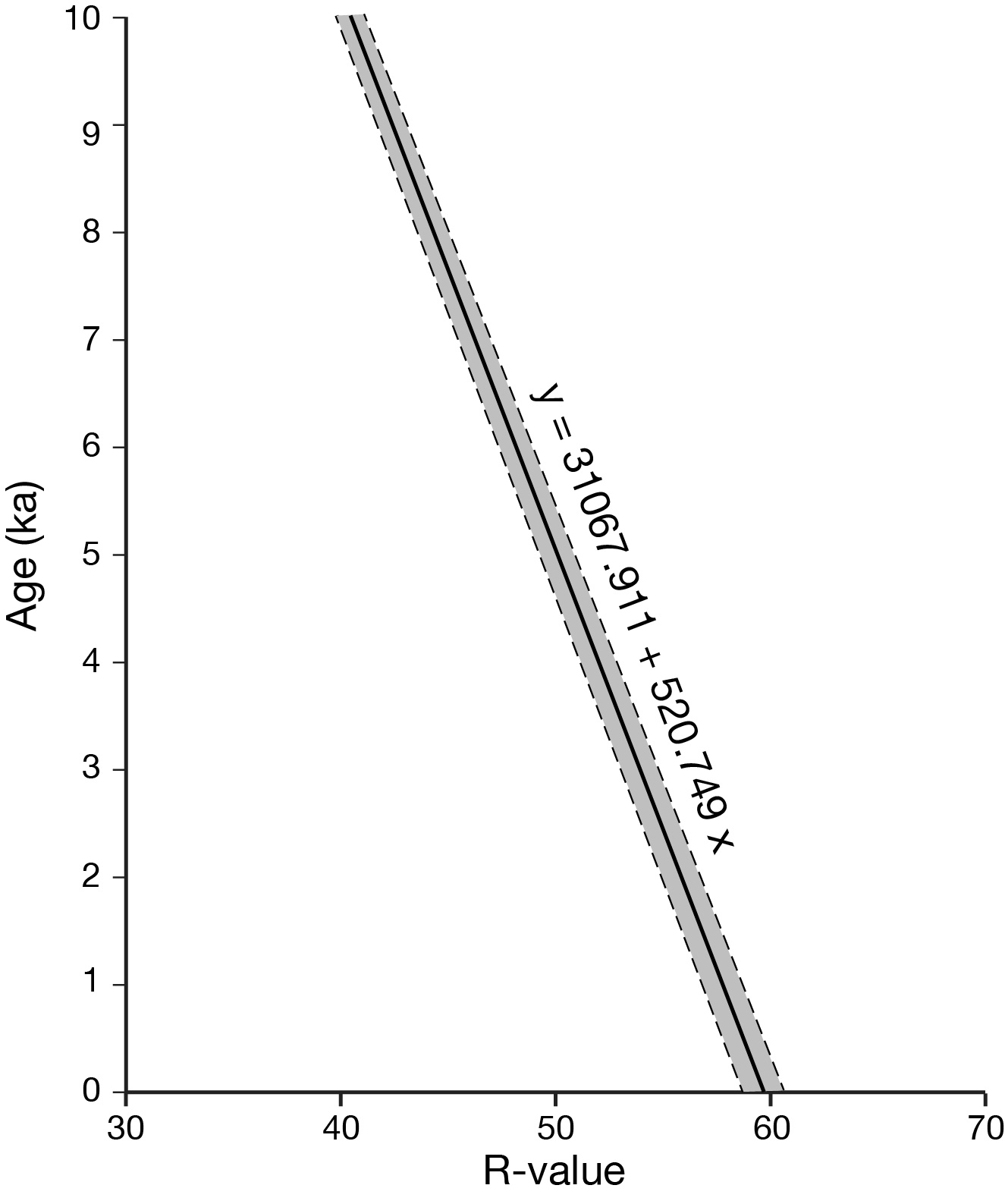
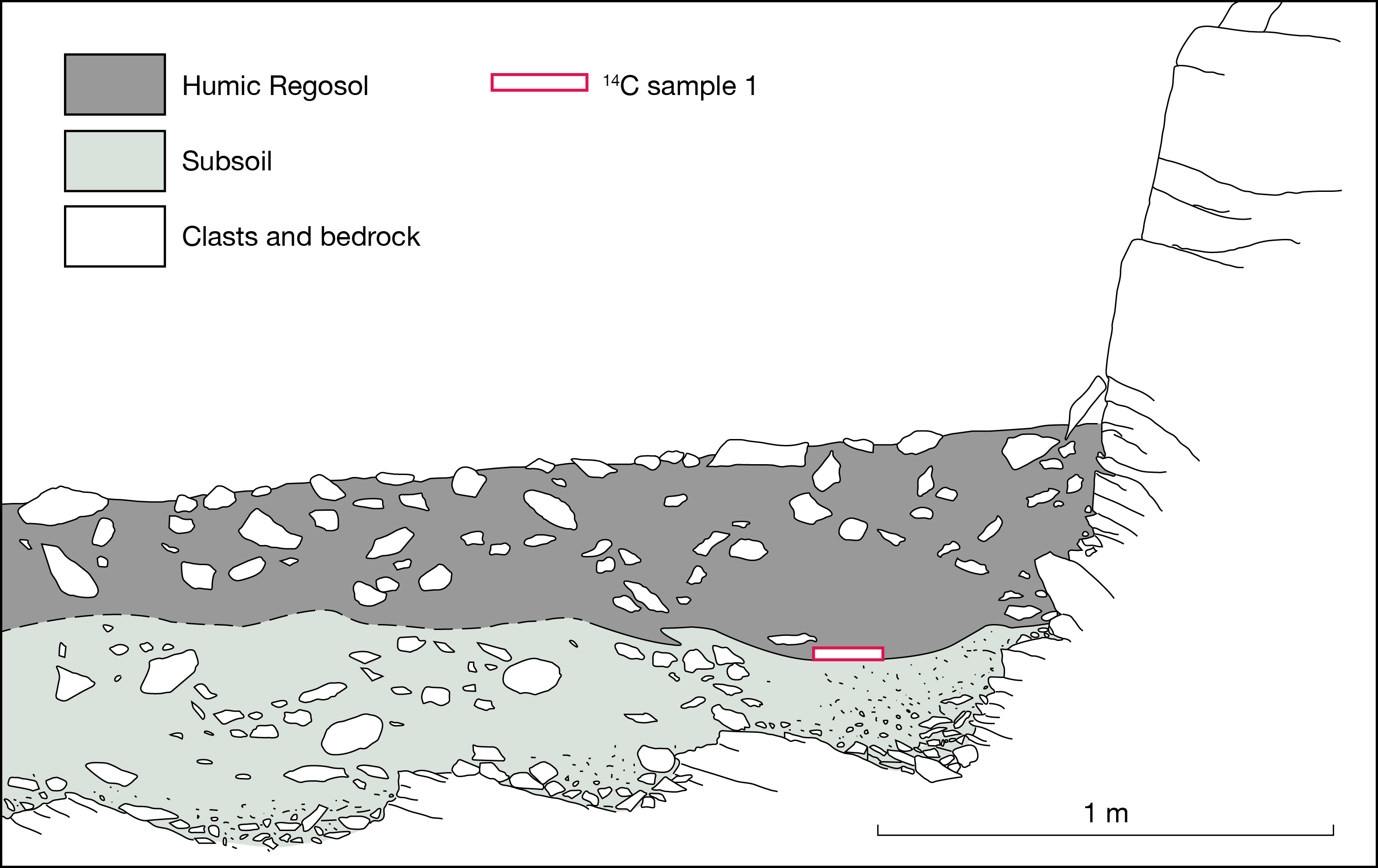
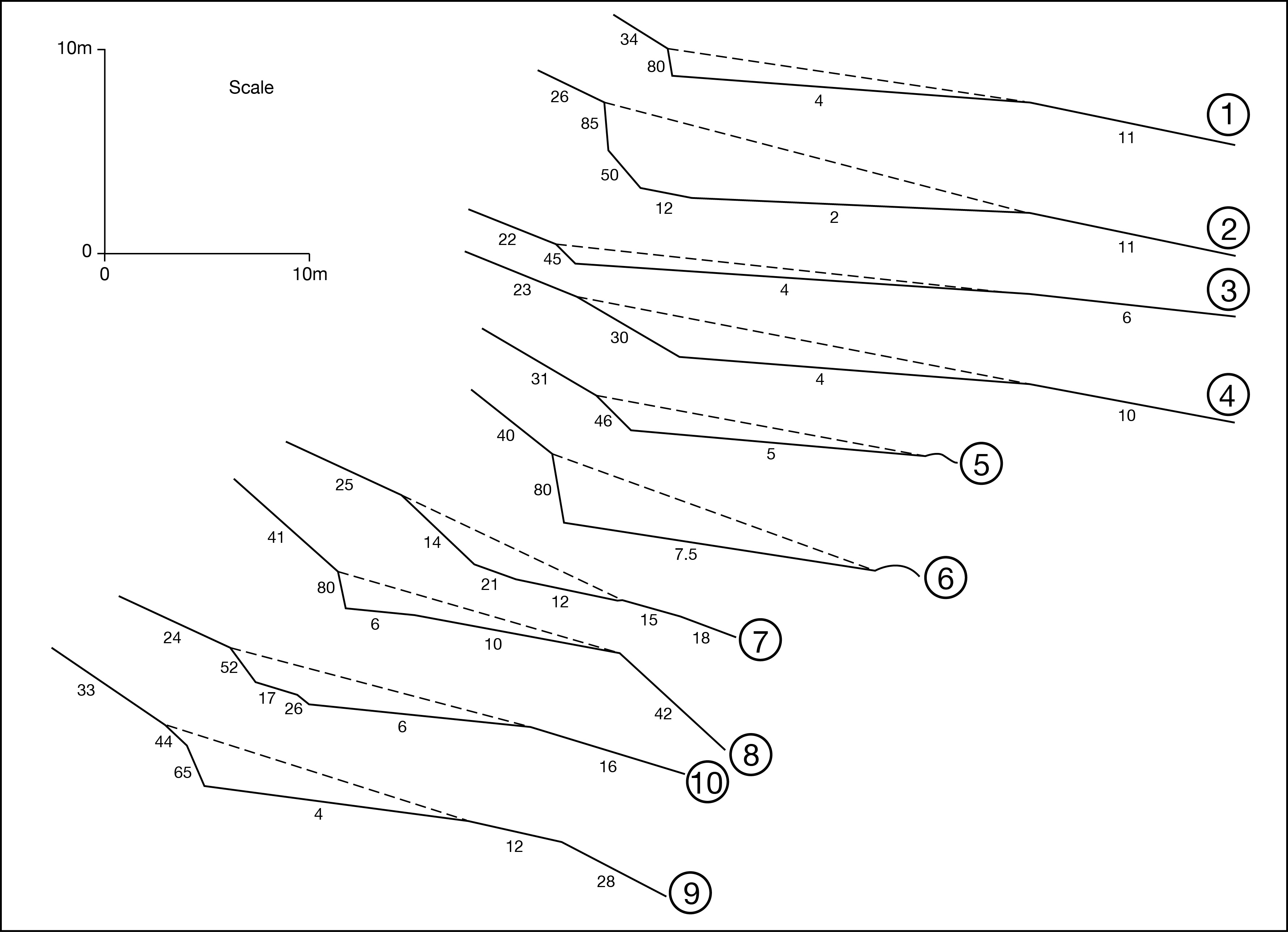
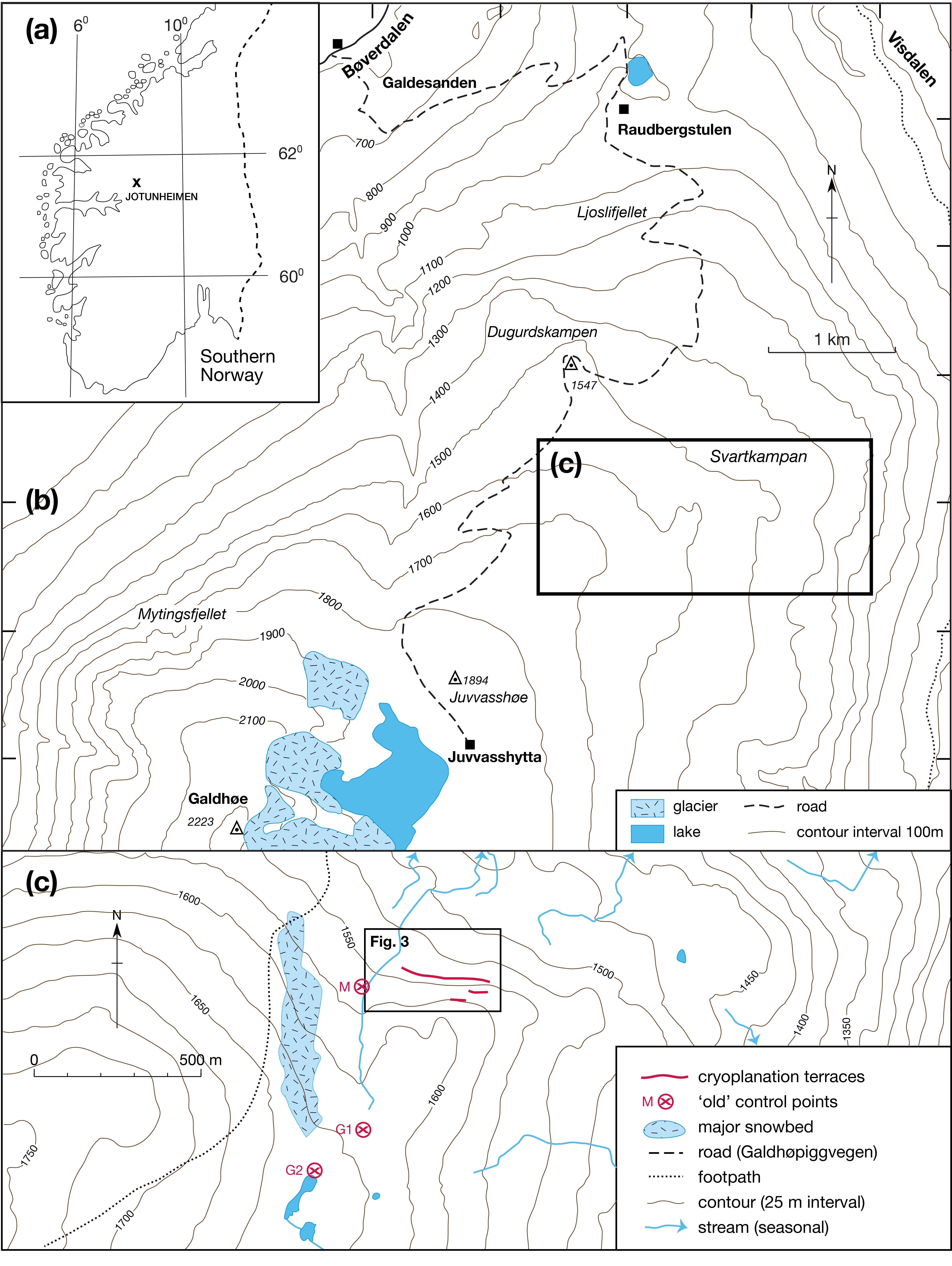
Schmidt-hammer exposure-age dating (SHD) of boulders on cryoplanation terrace treads and associated bedrock cliff faces revealed Holocene ages ranging from 0 ± 825 to 8890 ± 1185 yr. The cliffs were significantly younger than the inner treads, which tended to be younger than the outer treads. Radiocarbon dates from the regolith of 3854 to 4821 cal yr BP (2σ range) indicated maximum rates of cliff recession of ~0.1 mm/year, which suggests the onset of terrace formation prior to the last glacial maximum. Age, angularity and size of clasts, together with planation across bedrock structures and the seepage of groundwater from the cliff foot, all support a process-based conceptual model of cryoplanation terrace development in which frost weathering leads to parallel cliff recession and hence terrace extension. The availability of groundwater during autumn freeze-back is viewed as critical for frost wedging and/or the growth of segregation ice during prolonged winter frost penetration. Permafrost promotes cryoplanation by providing an impermeable frost table beneath the active layer, focusing groundwater flow, and supplying water for sediment transport by solifluction across the tread. Snowbeds are considered an effect rather than a cause of cryoplanation terraces and cryoplanation is seen as distinct from nivation.
| Journal Article Type | Article |
|---|---|
| Acceptance Date | Jun 13, 2019 |
| Online Publication Date | Sep 9, 2019 |
| Publication Date | Nov 1, 2019 |
| Deposit Date | Jun 18, 2019 |
| Publicly Available Date | Mar 10, 2020 |
| Journal | Quaternary Research |
| Print ISSN | 0033-5894 |
| Electronic ISSN | 1096-0287 |
| Publisher | Cambridge University Press (CUP) |
| Peer Reviewed | Peer Reviewed |
| Volume | 92 |
| Issue | 3 |
| Pages | 641-664 |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1017/qua.2019.41 |
| Keywords | cryoplanation terraces, Schmidt-hammer exposure-age dating, mountain permafrost, periglacial processes, alpine landform development, frost weathering, nivation |
| Public URL | https://uwe-repository.worktribe.com/output/1492860 |
| Contract Date | Jun 18, 2019 |
Files
Cryoplanation - final accepted manuscript (3).pdf
(806 Kb)
PDF
Licence
http://www.rioxx.net/licenses/all-rights-reserved
Copyright Statement
This is the author's accepted manuscript. Not for re-distribution or re-use. © copyright holder. The final published version is available online at: https://doi.org/10.1017/qua.2019.41
Cryoplanation Table 5.doc
(26 Kb)
Document
Cryoplanation Table 4.doc
(26 Kb)
Document
Cryoplanation Table 3.doc
(25 Kb)
Document
Cryoplanation Table 2.doc
(26 Kb)
Document
Cryoplanation Table 1.doc
(26 Kb)
Document
Cryoplanation fig 14 revised.jpg
(2.6 Mb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 13 revised.jpg
(308 Kb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 12.jpg
(352 Kb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 11.jpg
(168 Kb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 10.jpg
(141 Kb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 9.jpg
(357 Kb)
Image
Cryoplanation Fig 8.JPG
(5.2 Mb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 7.jpg
(618 Kb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 6a-d.jpg
(1.4 Mb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 5a-d.jpg
(1.3 Mb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 4.jpg
(547 Kb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 3.jpg
(2.5 Mb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 2a-b revised.jpg
(8.1 Mb)
Image
Cryoplanation fig 1 revised.jpg
(1.9 Mb)
Image
You might also like
EXCAVATIONS AT CATHOLE CAVE, GOWER, SWANSEA
(2014)
Journal Article